Gasoline Cars vs Electric Cars
The key differences between gasoline cars and electric cars, examining their performance, environmental impact, cost considerations, and infrastructure requirements.

Introduction:
The automobile industry is undergoing a significant transformation as electric vehicles (EVs) gain traction and challenge the dominance of traditional gasoline-powered cars. One of the key areas where these two types of vehicles often go head-to-head is performance. Here, we will compare the performance between gasoline cars and electric cars, exploring their respective strengths, weaknesses, and how they stack up against each other.
Which One to Pick?
Gas:
Gasoline cars, also known as petrol cars or internal combustion engine (ICE) cars, have long been admired for their power and performance capabilities. These vehicles utilize an internal combustion engine that burns gasoline or petrol fuel to generate power. The power output of a gasoline car is measured in horsepower (hp) or kilowatts (kW), and it largely depends on the engine's design and specifications.
Gasoline cars are known for their ability to deliver impressive power. They typically feature engines with multiple cylinders, such as 4, 6, or 8 cylinders, which allow for efficient combustion and power production. This configuration enables the engine to generate higher horsepower and torque, resulting in excellent acceleration and high top speeds. The responsive throttle of a gasoline car allows drivers to experience quick bursts of speed, making them suitable for overtaking on highways or enjoying spirited driving on winding roads.

In terms of performance, gasoline cars excel at delivering thrilling acceleration. The combustion process in the internal combustion engine allows for the rapid release of energy, translating into swift acceleration from a standstill. With higher horsepower engines, gasoline cars can achieve impressive acceleration times, propelling occupants forward with a surge of power. Additionally, gasoline cars are engineered to provide engaging driving dynamics, featuring suspension systems, chassis designs, and weight distribution optimized for a balance between comfort and sportiness. The combination of precise steering, responsive handling, and the ability to handle various road conditions contributes to an immersive and enjoyable driving experience.
Or
Electric(EV):
Electric cars have emerged as a transformative force in the automotive industry, offering a cleaner and more sustainable mode of transportation. These vehicles are powered by electric motors that run on electricity stored in high-capacity batteries.
Electric cars are known for their environmental friendliness. Unlike gasoline cars, they produce zero tailpipe emissions, helping to reduce air pollution and combat climate change. By replacing fossil fuel combustion with electricity, electric cars significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a cleaner and healthier environment. The use of renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, for charging further enhances their sustainability.

In addition to their environmental benefits, electric cars offer impressive performance capabilities. Electric motors provide instant torque delivery, delivering immediate and seamless acceleration from a standstill. This characteristic provides a smooth and responsive driving experience that can be particularly enjoyable in urban environments. Moreover, electric cars typically have a lower center of gravity due to the battery placement, enhancing stability and handling. The even weight distribution from the battery pack contributes to improved balance, making electric cars agile and nimble on the road. With advancements in technology, electric cars are also offering longer driving ranges and faster charging times, making them more practical for everyday use and long-distance travel.
Changes in the Market:
For a long time, electric vehicles struggled to overtake their gas-powered counterparts both at the filling station and on the freeway. But innovation in the EV market means that electric cars are becoming quicker, more economical, and more affordable, not to mention more environmentally friendly than automotive engineering. We have now reached a point where people are starting to take note of the benefits of electric cars, whether as personal vehicles, corporate fleets, and even EV rentals.
This, coupled with the fact that some states in the US have announced plans to ban sales of new gasoline vehicles in the next decade, means more drivers are choosing to go electric, and EV registrations in the US are always on the rise, and while electric vehicles still make up only 4.6% of the new car market, that number looks set to increase as more people see the benefits of switching.
Things You Should Consider Before Making the Final Decision:
If you’re considering an electric car as your next vehicle for your driveway or your next business rental, it’s important to understand the main differences between EVs and gas vehicles, and the pros and cons of electric cars.
KEY DIFFERENCES:
Power and Acceleration:
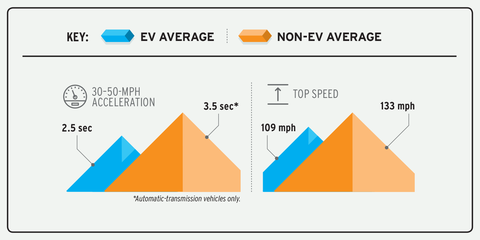
Gasoline Cars: For decades, gasoline cars have been synonymous with power and speed. Equipped with internal combustion engines, they offer high horsepower and torque, allowing for exhilarating acceleration and top speeds. The roar of a V8 engine and the thrill of pushing a gasoline car to its limits have long been part of automotive culture.
Electric Cars: While electric cars may not have the same raw power as their gasoline counterparts, they excel in instant torque delivery. Electric motors offer immediate acceleration from a standstill, resulting in impressive 0-60 mph times. Many high-performance electric cars, such as Tesla's Model S Plaid, have shattered acceleration records, leaving even the fastest gasoline cars in their dust.
Handling and Driving Dynamics:
Gasoline Cars: Gasoline cars have benefited from decades of engineering refinement in terms of suspension, steering, and chassis design. Their driving dynamics often provide a more engaging and connected experience, with precise handling and feedback. Enthusiasts appreciate the balance between power and control that gasoline cars offer, making them the preferred choice for spirited driving.
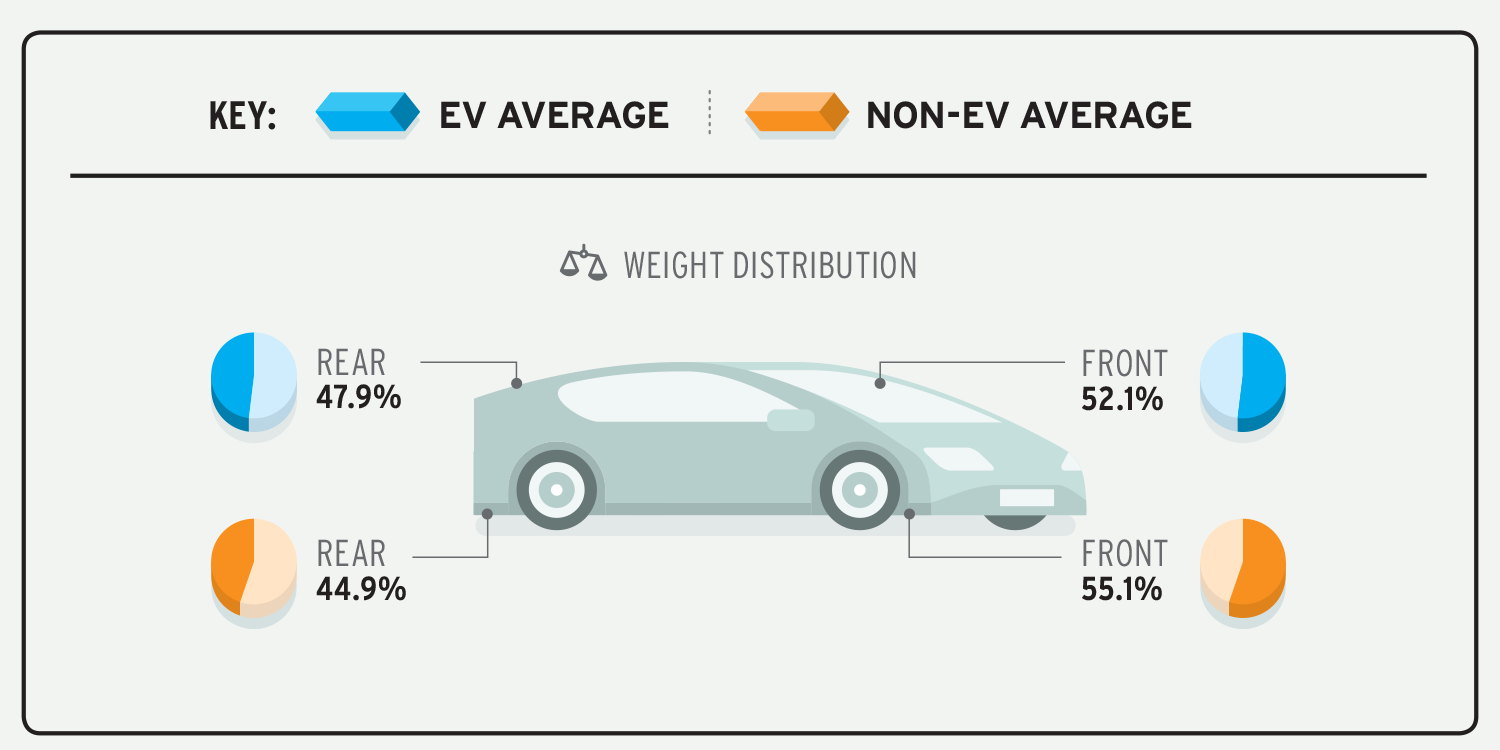
Electric Cars: Electric cars have a distinct advantage when it comes to handling due to their low center of gravity. With heavy battery packs located beneath the vehicle, electric cars exhibit excellent weight distribution, resulting in improved stability and cornering abilities. Additionally, electric cars can distribute torque to individual wheels, enabling advanced traction control systems for enhanced grip and control on the road.
Maintenance and Reliability:
Gasoline Cars: Gasoline cars rely on complex internal combustion engines with numerous moving parts that require regular maintenance. Oil changes, spark plug replacements, and other maintenance tasks are common, and the potential for mechanical issues and breakdowns increases with age. However, gasoline cars benefit from a well-established network of repair shops and readily available spare parts.
Electric Cars: Electric cars have a simpler drivetrain with fewer moving parts, leading to lower maintenance requirements. With no oil changes, timing belts, or exhaust systems to worry about, the cost and frequency of maintenance are generally reduced. Electric motors are also known for their durability and reliability, with fewer components prone to failure. However, the availability of qualified technicians and specialized repair facilities may be limited in some areas.

Environmental Impact:
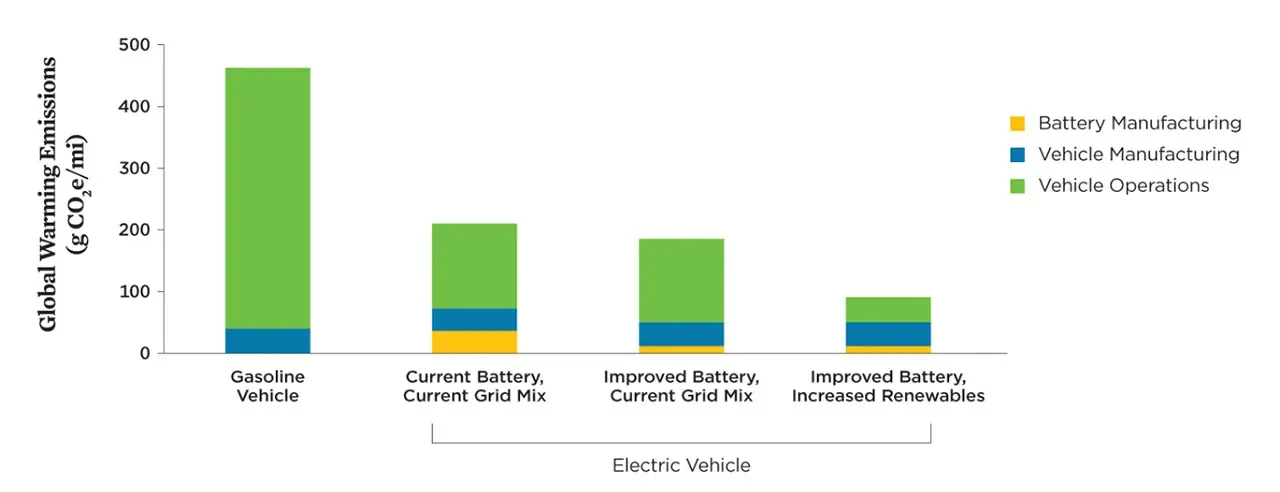
Gasoline Cars: Gasoline cars have long been associated with environmental concerns due to their emissions. Internal combustion engines burn fossil fuels, releasing greenhouse gases and contributing to air pollution. However, advancements in fuel efficiency and the adoption of hybrid technologies have mitigated some of these environmental impacts.
Electric Cars: Electric cars produce zero tailpipe emissions, as they are powered by electricity stored in their batteries. By reducing or eliminating reliance on fossil fuels, electric cars offer a greener and more sustainable transportation alternative. Their environmental impact is directly tied to the source of electricity generation, with renewable energy options providing the most significant benefits.
Pros and Cons of Gasoline Cars:
Pros:
- Power and Performance: Gasoline cars are known for their high horsepower and torque, providing thrilling acceleration and top speeds.
- Wide Availability: Gasoline fuel is widely available, with a well-established infrastructure of gas stations.
- Longer Driving Range: Gasoline cars typically offer a longer driving range compared to electric cars, allowing for extended road trips without frequent refueling.
- Quick Refueling: It takes just a few minutes to refuel a gasoline car, offering convenience and reducing downtime during long journeys.
- Established Maintenance Network: Gasoline cars benefit from an extensive network of repair shops and readily available spare parts, making maintenance and repairs more accessible.
Cons:
- Environmental Impact: Gasoline cars emit greenhouse gases and contribute to air pollution due to the combustion of fossil fuels.
- Reliance on Fossil Fuels: Gasoline cars are dependent on a finite and non-renewable resource, contributing to concerns about energy security and price volatility.
- Higher Operating Costs: Gasoline prices can fluctuate, and the cost of fueling a gasoline car is generally higher than charging an electric car.
- Maintenance and Complexity: Gasoline cars have complex internal combustion engines with many moving parts, leading to higher maintenance and repair costs.
- Noise Pollution: The rumble and engine noise of gasoline cars may be undesirable to some individuals, particularly in urban environments.
Pros and Cons of Electric Cars:
Pros:
- Environmental Benefits: Electric cars produce zero tailpipe emissions, helping to reduce air pollution and combat climate change.
- Energy Efficiency: Electric motors are more energy-efficient compared to internal combustion engines, resulting in lower energy consumption and operating costs.
- Instant Torque and Acceleration: Electric cars deliver instant torque, providing quick and smooth acceleration from a standstill.
- Quieter Operation: Electric cars produce minimal noise, contributing to a quieter and more peaceful driving experience.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: Electric cars have fewer moving parts and require less maintenance compared to gasoline cars, leading to potential cost savings.
Cons:
- Limited Driving Range: Electric cars typically have a shorter driving range compared to gasoline cars, requiring more frequent charging or access to charging infrastructure.
- Charging Infrastructure: The availability of charging stations can be limited in certain areas, potentially causing range anxiety for electric car owners.
- Longer Refueling Time: Charging an electric car takes considerably longer than refueling a gasoline car, requiring planning and patience for longer trips.
- Upfront Cost: Electric cars often have a higher upfront purchase cost compared to gasoline cars, although government incentives and declining battery prices are helping to narrow the gap.
- Battery Degradation: Over time, the capacity and performance of electric car batteries may degrade, reducing driving range and requiring eventual replacement.
Conclusion:
The competition between gasoline cars and electric cars represents a critical turning point in the automotive industry. While gasoline cars continue to offer power and a familiar driving experience, electric cars provide cleaner transportation options with instant torque and sustainability benefits. As technology advances, electric cars are becoming more appealing with improved range, faster charging, and declining costs. Ultimately, the choice between gasoline and electric cars depends on individual preferences, driving needs, and environmental considerations, and both have their merits in the ever-evolving landscape of transportation.





