Europe Going All Out in EV Starting 2035
Mandating zero CO2 emissions from all new cars by 2035 demonstrates a bold commitment.

The global push towards decarbonization and sustainable transportation is at a crucial juncture, with the European Union (EU) and also the United States (U.S.) making significant strides towards phasing out carbon dioxide-emitting vehicles. In this blog, we'll explore the latest developments in both regions, examining policies, challenges, and the path forward in transitioning to a zero-emission vehicle future.
Europe's Ambitious Roadmap
Europe's recent approval of a law to cease the sale of new CO2-emitting cars by 2035 represents a watershed moment in the region's climate policy. Given that transportation contributes nearly a quarter of EU emissions, this decisive action underscores the EU's determination to address climate change head-on. Mandating zero CO2 emissions from all new cars by 2035 demonstrates a bold commitment to reducing carbon footprints and transitioning towards sustainable transportation solutions. However, while this ambitious roadmap sets a clear direction, it also presents a myriad of challenges. From technological barriers to economic considerations, the transition to zero-emission vehicles requires comprehensive strategies and robust collaboration between governments, industries, and stakeholders.

One of the primary challenges facing Europe's ambitious roadmap is the need for widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and other alternative propulsion technologies. While EVs offer a promising solution to decarbonize transportation, obstacles such as affordability, charging infrastructure, and consumer acceptance persist. Additionally, the exemption allowing cars running on e-fuels beyond 2035 raises questions about the scalability and environmental impact of such technologies. Overcoming these challenges will require concerted efforts to invest in innovation, incentivize EV adoption, and address regulatory complexities to ensure a smooth transition towards a greener, more sustainable automotive sector.
Key Challenges and Controversies
Germany's successful negotiation for an exemption permitting cars fueled by e-fuels beyond 2035 underscores the intricate nature of the transition towards zero-emission vehicles. While e-fuels present a promising alternative for traditional vehicles, their scalability and environmental ramifications are subject to debate. Questions linger regarding the efficiency of e-fuels in significantly reducing carbon emissions and their overall sustainability compared to battery-electric vehicles. Poland's resistance to the law and reservations expressed by other EU member states emphasize the imperative for cohesive and inclusive policymaking. Achieving consensus among diverse stakeholders is essential to navigate the complexities of transitioning towards a cleaner automotive industry while addressing varied concerns and priorities across the European Union.

The controversy surrounding the exemption for e-fuels beyond 2035 reflects broader debates within the EU regarding the most effective strategies to combat climate change and decarbonize transportation. While some advocate for a gradual transition incorporating multiple technologies, others emphasize the urgency of accelerating the adoption of pure electric vehicles to meet ambitious emissions targets. Striking a balance between innovation, environmental impact, and economic considerations is paramount in crafting effective policies that drive sustainable mobility. As the automotive industry undergoes profound transformation, policymakers must engage in transparent dialogue and holistic decision-making processes to navigate challenges, address controversies, and ensure a smooth transition towards a greener future for European transportation.
The Role of Electric Vehicles in Europe
Despite ongoing controversies surrounding alternative fuels like e-fuels, electric vehicles (EVs) maintain a pivotal role in Europe's overarching strategy for decarbonization. The European Union's ambitious target of attaining 80% EV sales by 2030 signals a resolute commitment towards sustainable mobility. However, achieving this goal poses multifaceted challenges that necessitate comprehensive solutions. Affordability remains a significant barrier to widespread EV adoption, particularly for consumers from diverse socioeconomic backgrounds. Moreover, the development of robust charging infrastructure across urban and rural areas is essential to alleviate range anxiety and facilitate long-distance travel. Addressing these challenges requires concerted efforts from policymakers, manufacturers, and other stakeholders to implement effective strategies that promote affordability, accessibility, and consumer confidence in EV technology.
Investments in research, development, and incentives are fundamental pillars in accelerating mass-market EV adoption across Europe. Continued innovation in battery technology, vehicle design, and manufacturing processes is crucial to enhance the performance, affordability, and sustainability of electric vehicles. Moreover, governments and private sector entities must collaborate to establish supportive regulatory frameworks and financial incentives that encourage consumers to transition towards EVs. By fostering a conducive ecosystem for EV innovation and adoption, Europe can position itself as a global leader in sustainable transportation while advancing towards its climate goals.
Lessons from the U.S.
In the United States, the momentum behind phasing out gas-powered cars is palpable, albeit with distinctive approaches compared to Europe. President Biden's executive order, which establishes a target for half of all new vehicle sales to be zero-emission by 2030, underscores a robust commitment to advancing electric vehicles (EVs) and combating climate change. This executive action reflects a significant shift in federal policy towards prioritizing clean energy and sustainable transportation solutions. Furthermore, the coordinated efforts of several states, such as California and New York, in implementing bans on new gas-powered vehicle sales by 2035 demonstrate a decentralized yet synchronized approach towards decarbonization. These state-level initiatives not only align with federal goals but also showcase the importance of subnational action in driving progress towards emissions reductions and environmental sustainability.
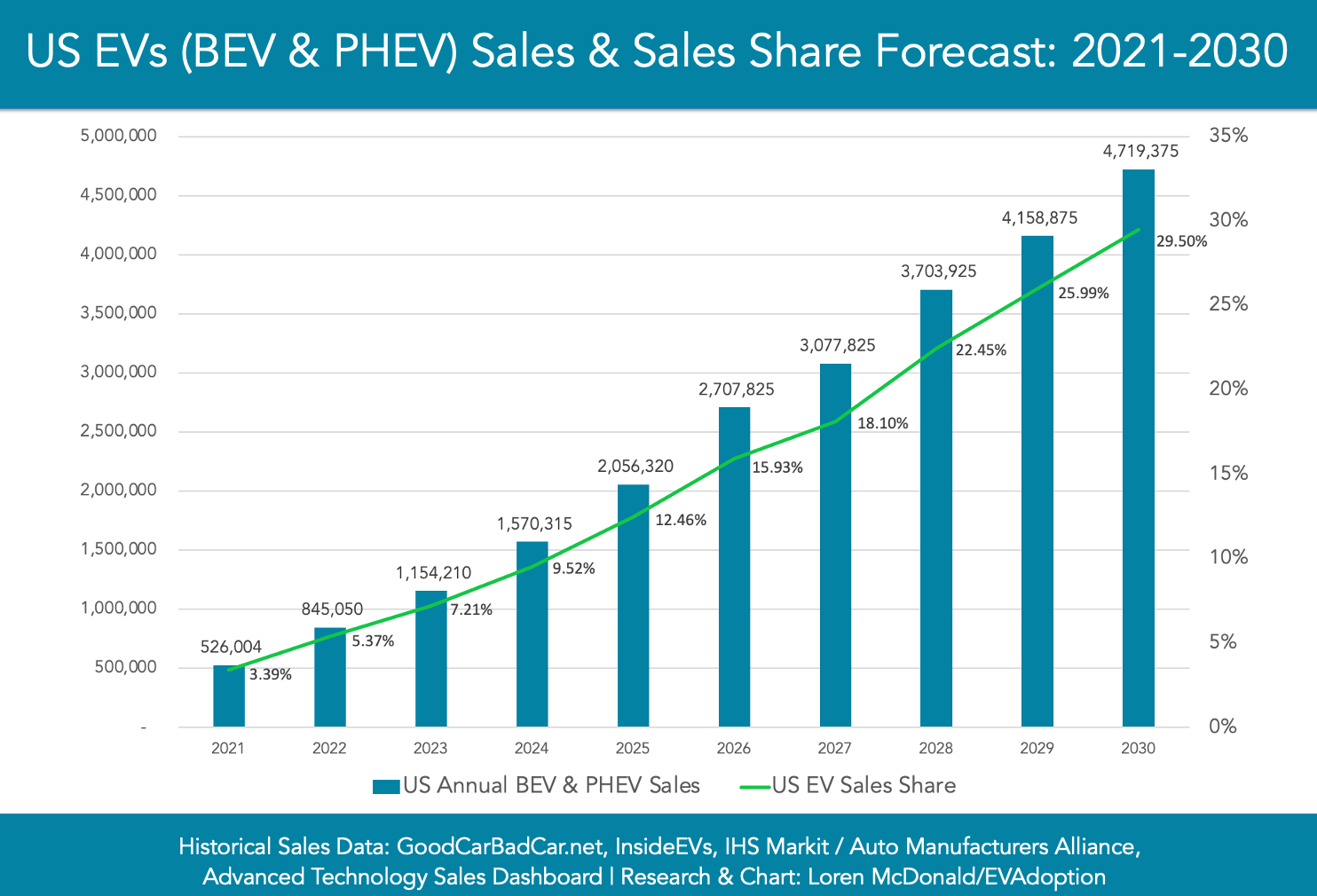
Despite the progress made at the federal and state levels, the transition to zero-emission vehicles in the United States faces notable challenges. While ambitious targets and regulatory measures set the stage for EV adoption, barriers such as infrastructure limitations, consumer adoption rates, and industry dynamics must be addressed. Investments in charging infrastructure expansion, financial incentives for consumers and manufacturers, and public education campaigns are essential to overcoming these obstacles. Additionally, fostering collaboration between governments, private sectors, and stakeholders will be critical in navigating the complexities of the transition and ensuring a smooth and equitable shift towards a greener automotive future in the United States.
Challenges and Opportunities
The transition towards electric vehicles (EVs) presents promising opportunities for reducing emissions and advancing sustainable mobility, yet it is not without its challenges. High upfront costs, stemming from factors such as battery technology expenses, pose a significant barrier to widespread EV adoption. Additionally, supply chain dependencies, particularly concerning critical materials like lithium and cobalt, underscore the need for diversification and sustainable sourcing practices.
Moreover, the presence of charging infrastructure gaps, especially in rural and less populated areas, hinders the mainstream acceptance of EVs. Addressing these challenges will necessitate robust collaboration between governments, industries, and stakeholders to implement comprehensive solutions that ensure a smooth transition towards a greener automotive future.
The Role of Innovation and Policy
In both Europe and the United States, innovation and policy play complementary roles in propelling the transition towards zero-emission vehicles. Strategic investments in battery technology, renewable energy infrastructure, and forward-thinking regulatory frameworks are pivotal for expediting advancements in the EV market. These initiatives not only facilitate the development of more efficient and affordable electric vehicles but also contribute to the establishment of a sustainable energy ecosystem.
Furthermore, fostering a supportive environment for research, development, and entrepreneurship is paramount in stimulating innovation and unlocking novel solutions to tackle the multifaceted challenges associated with the transition to greener transportation. By integrating innovation-driven policies and fostering collaboration between public and private sectors, both Europe and the U.S. can pave the way for a more sustainable and resilient automotive industry.





